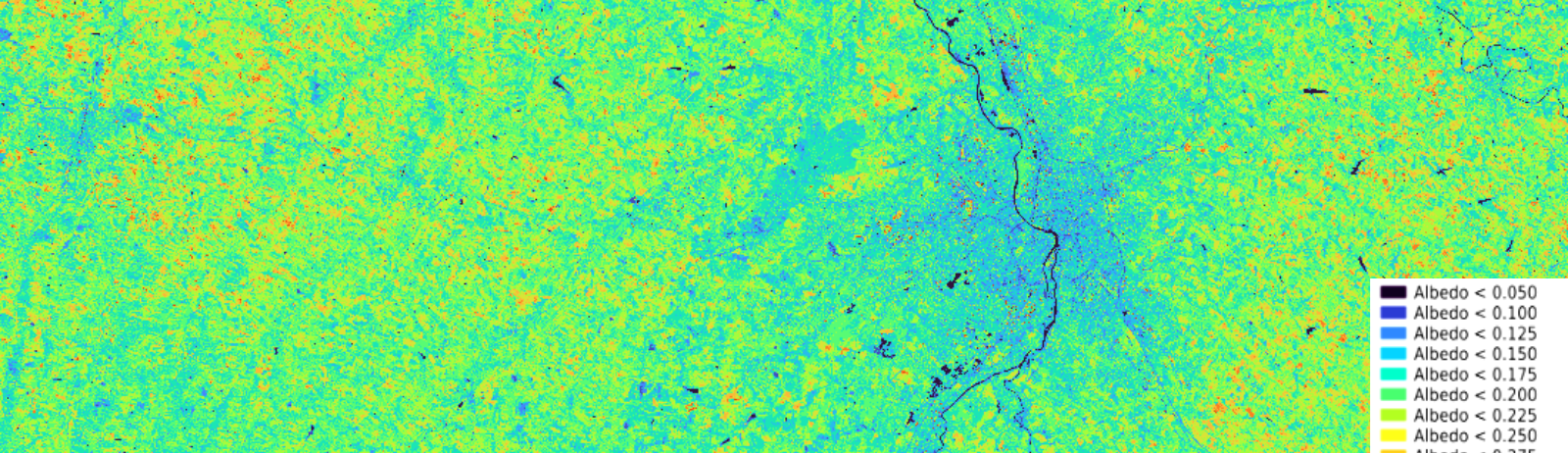
Data access
Description
Albedo is an essential climatic variable (ECV) defined by the hemispherical or bi-hemispherical light energy flux reflected in relation to the incident flux. Several angular sighting and solar observations are required to obtain it, and BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) models are commonly used to reconstitute the complete directional spectrum from a few space observations. Spectral integration from Sentinel-2 spectral albedos is used to estimate the solar albedo.
Albedo is the third lever for mitigating global warming, after reducing greenhouse gases and storing carbon in the soil. It highlights the reflective power of surfaces to reduce heat storage. The ALBEDO-prairies project, led by IDELE (Institut de l’Élevage – Livestock Institute ) and financed by CASDAR (Special Appropriation Account for Agricultural and Rural Development), supported the development of a HR (High Resolution) albedo product to demonstrate the “cooling” effect of grasslands. The SCO SatBDNB (National Building Database) project, piloted by the CSTB (Centre Scientifique et Technique du Bâtiment – Scientific and Technical Building Center), then made the method operational and ensured initial national production. A better understanding of albedo in urban environments also means a better understanding of urban heat islands (UHIs), and thus a better prioritization of building retrofits.
Data and methods
The albedo calculation method breaks down as follows:
- Use as input of MAJA data from the cloud detection and atmospheric correction chain designed to produce surface reflectances (level 2A) from level 1C orthorectified satellite images, here Sentinel-2 images.
- Application of a per-pixel BRDF model to a time series of Sentinel-2 data for directional integration
- Solar spectrum integration of Sentinel-2 albedos for bands B2, B4, B8A and B11
This is an adaptation of a method developed for PROBA-V as part of the Copernicus Global Land Service (CGLS) (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.05.015).
The products generated correspond to an albedo over the period June-September 2022. They include an uncertainty that takes into account the number of data sets and the diversity of angular sampling.
The product has already been used as part of the ALBEDO-prairies project, for which it was validated on the basis of albedometers installed on grasslands.
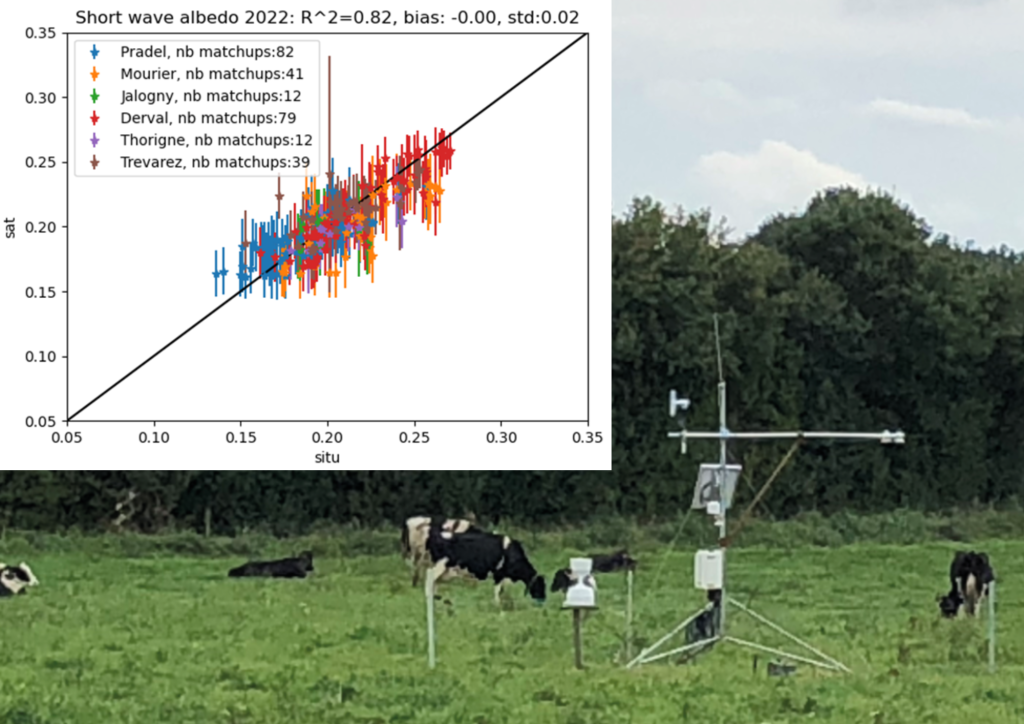
Albedo is used to assess the negative radiative forcing of grasslands and convert it into carbon fluxes to offset emissions. The next step is the CASDAR ALBAATRE project (“ALBédo”, a means of mitigating and adapting to global warming through forage cropping systems for ruminant livestock.) starting in January 2024, which will focus on the most resilient and reflective species.
The SCO SatBDNB project will also be followed up by the ADEME Surcarto project for the “Plus fraîche ma ville” program, which will use multi-year albedo production to assess changes in UHI in France.
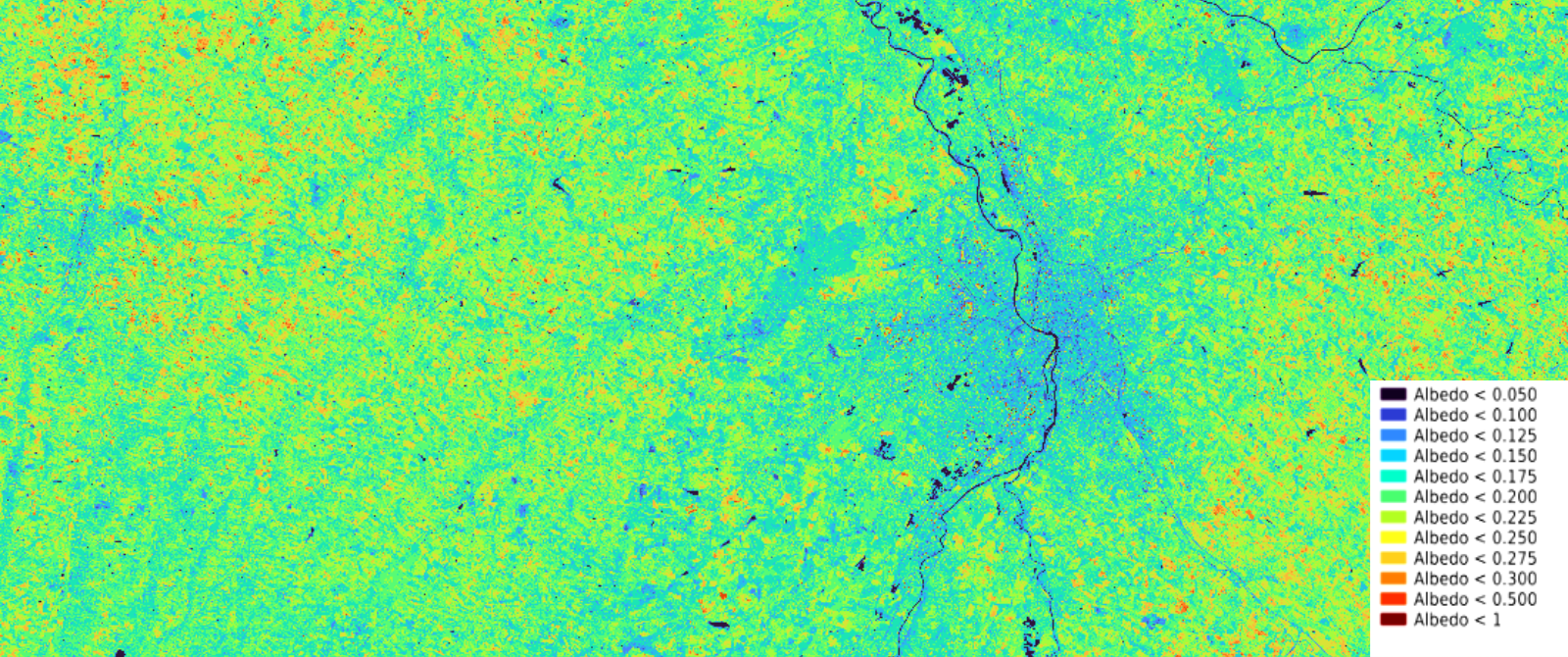
Values range from 0.12 (dark pixels) to 0.27 (red pixels).
Contact

Jean-Louis Roujean
CESBIO
@J-L.Roujean
Références
Jean-Louis Roujean, Jonathan Leon-Tavares, Bruno Smets, Patrick Claes, Fernando Camacho De Coca, Jorge Sanchez-Zapero, Surface albedo and toc-r 300 m products from PROBA-V instrument in the framework of Copernicus Global Land Service, Remote Sensing of Environment, Volume 215,
2018, Pages 57-73, ISSN 0034-4257, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2018.05.015.